Android application development has come a long way with all the new technologies, languages and platforms being updated every now and then. You have yourself experienced regular updates in the applications in your android phones, how they have changed overtime, from the interface to user experience and many other features. Initially, only java was used to Create Android applications, now Kotlin, an open source and easy to use language has also become an option for the developers.
Java for android development
Java is being used by the android application developers since inception as it is the only language used for the same. Those who are familiar with the language know in and out of it. For those who are new to it, Java is an object oriented programming language that was launched in 1995. It is mostly used for standalone and backend development. Android is also written in Java, therefore, it is the first choice of the developers for creating android applications.
Kotlin: More stable and congruous
Kotlin programming language gained its name from the Kotlin Island near St. Petersburg. Though, Kotlin appeared in 2011, its v1.0 was officially launched in 2016 and is being updated since then. It is a concise, cross platform development programming language. Although, it has been designed to interoperate with Java, Kotlin is used as a complete new alternative by the application developers.
In Kotlin V1.2 the feature of sharing code between JVM and javaScript was added. Then came V1.3 with coroutines for asynchronous programming. In 2017, Google announced that Kotlin could be a preferred language for android application development.
Kotlin compared to java:
Both the languages are useful in their own way. Some features and coding changes in Kotlin have made it even more popular among the developers.
Have a look at the two codes below:
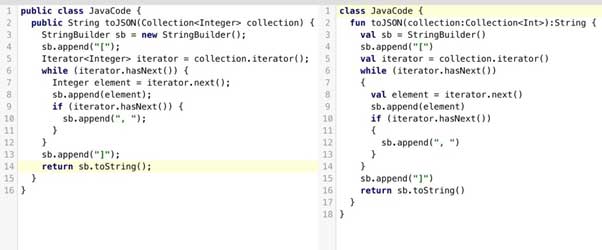
Those familiar with both these languages will know what the difference is. To make it clear, the code on the left is in Java and the other one is a bit tweaked in Kotlin. Kotlin is more streamlined and concise as compared to Java. You can see in the code on the right, functions are defined with the fun keyword, and semicolons are optional at the end. The val keyword declares a read-only property or local variable in Kotlin. These are a few changes, there are many more differences and special features that make Kotlin a much user friendly language.
Let’s go through the features one by one.
1) NullPointerException
In Java, the user is allowed to assign null value to any variable but while accessing any object reference which has been assigned a null value, raises exception. The developer then has to handle the exception and this may lead to a lot of delay and frustration. In Kotlin, every variable and object is non nullable by default. It means the user cannot assign any null value, if tried, the program will fail while compiling. If there is any requirement then the user can assign a null value to the variable as:
val num : int ? = nul
2) Coroutines-What are these?

This is an example of how coroutines are written in Kotlin coding. The code clearly defines the terms of a coroutine. It is another great feature of Kotlin. The support of coroutines helps in executing long runtime operations by suspending the execution at a certain point without blocking the threads. Coroutines help in managing the task without any hassle. Android platform is single threaded by default but in case of longer runtime network I/O or CPU intensive operations, Java supports Android in creating multiple threads in the background. But this makes the task complex and sometimes it is unmanageable. Therefore, the role of Coroutines is important.
3) Smart Casts
In Kotlin there are smart casts that check the type and cast of the variable automatically. is or !is operator is used to check the type of variable, and compiler automatically casts the variable to the target type. In Java the user has to first check the type and caste of the variable for any operation.
Have a look at this code using ‘is’ operator in Kotlin for clear understanding:
un main(args: Array
val str1: String? = “Sentences”
var str2: String? = null // prints String is null
if(str1 is String) {
// No Explicit type Casting needed.
println(“length of String ${str1.length}”)
}
else {
println(“String is null”)
}
}
4) Extension Functions
There are no extension functions in Java. It means if the user has to extend the functionality of any function he/she will have to create a new class and inherit the parent class. Whereas, Kotlin provides the feature of extending the existing functions by prefixing the name of the class to the name of the new function. For example:
fun String.removeFirstLastChar(): String = this.substring(1, this.length – 1)
fun main(args: Array
val myString= “Hello Everyone”
val result = myString.removeFirstLastChar()
println(“First character is: $result”)
}
In the code above, fun String.removeFirstLastChar() is an extension function.
5) Data Classes
In Java if any class has to hold only data then we need to define constructers, variables to store data, getter() and setter() methods, hashcode(), ToString() and equals() function. In case of Kotlin if the class has to hold only data then it is defined with keyword data and the rest is taken care of by the compiler like creating constructors, getter(), setter() methods etc.
data class Person(var name: String, var surname: String, var id: String)
Where you see a single line written in Kotlin to use the data class, we require a bunch of code to use the data class in Java.
6) Type Inference
Every variable needs to be defined with its type explicitly when you are coding in Java. In case of Kotlin there is no compulsion to define the type of the variable. If you want you can always define explicitly.
You can freely write val str = “hello” in Kotlin
instead of val str : String = “hello” as used in Java
7) Functional Programming
Functions in Kotlin are considered as first-class values, it means they can be assigned to variables and shared to parameters. Java does not support functional programming. For android application development it only supports the subset of Java 8 features. Whereas Kotlin is a combination of both procedural and functional programming. It supports various methods like lambda, operator overloading, higher order functions and many more.
Conclusion
Kotlin and Java are both powerful programming languages with significant strengths. Kotlin provides a modern and developer-friendly experience with concise syntax and modern features. Java, on the other hand, remains a reliable choice for large-scale enterprise applications due to its extensive libraries and large-community support.
Kotlin JavaScript is based on JVM but can be compiled into JavaScript, Android, and Native application development too. The additional features have made Kotlin a feasible development language. Google also announced Kotlin as the official Android development programming language in its I/O keynote.
Comparatively, Java has retained its popularity as an exceptional general-purpose programming language. It has been actively used for Android and Native application development for decades and will not be replaced anytime soon.
In conclusion, the debate over which language is better is complex and will spark interesting discussions even in the future. Apart from language differences, factors like existing codebase, developer’s proficiency, and project requirements also back the right selection of a particular language for a specific project.




