Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, securing user identities is more critical than ever. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has emerged as a powerful process to enhance security by verifying user identities through various methods. Auth0 simplifies the implementation of MFA and Passwordless authentication, making it easier for developers to protect their applications.
Why MFA Matters?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that requires users to answer two or more confidential questions apart from entering their password to access a resource. By adding layers of verification, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and phishing attacks. This could be a combination of:
- Something you know (password)
- Something you have (phone or token)
- Something you are (biometric data)
Auth0 MFA Overview
Auth0 is a flexible identity platform that offers authentication, authorization, and user management services. Its MFA capabilities include:
- Universal Login: A ready-to-use login page with built-in MFA support.
- Custom UI: Dedicated pages to create tailored login experiences.
- Authentication Factors: Verification factors like email, one-time passwords (OTP), push notifications (via Guardian app), and SMS.
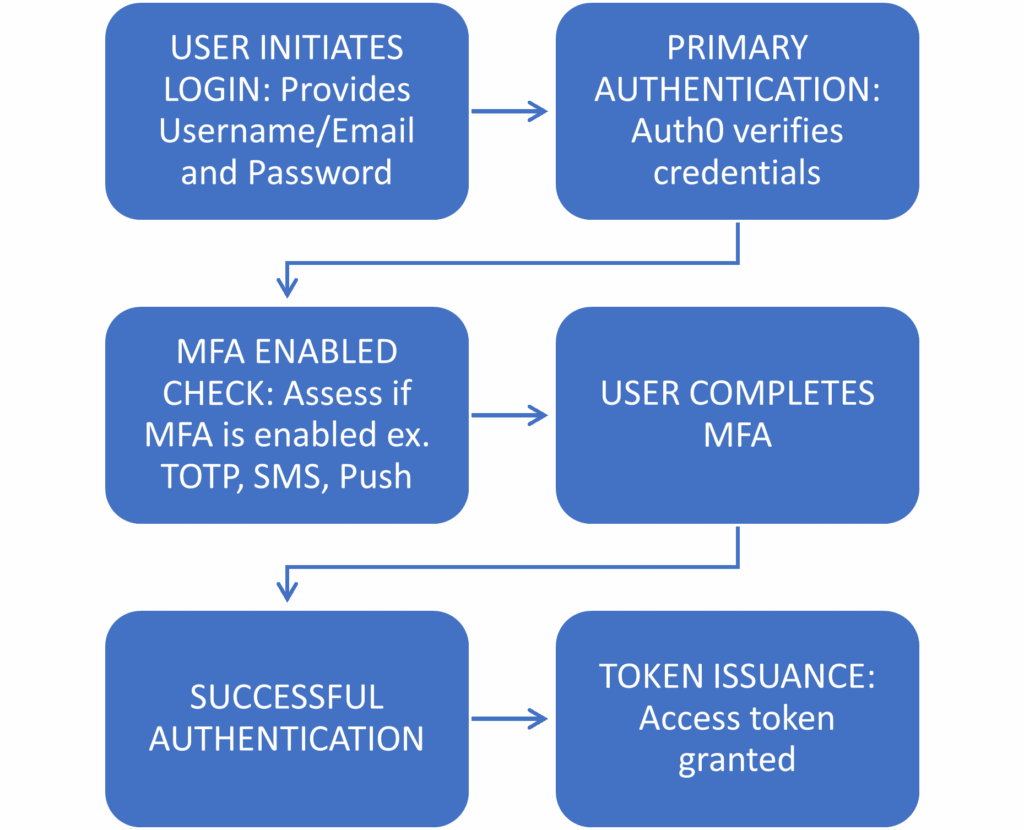
- Adaptive MFA: Also known as risk-based authentication, this security mechanism adjusts the verification process based on the context and user behavior. Instead of applying the same level of security to every login, it evaluates risk factors in real-time to adjust authentication steps accordingly.
Let’s take an example. An employee is trying to access their Microsoft 365 account. Depending on various factors, adaptive MFA can assess the level of risk as follows:
- Low-Risk Access: “The employee is working from office and tries to log in using a company-issued laptop”. In this case, only a password is required (password + trusted device = seamless login).
- Medium-Risk Access: The employee is working from home and attempts to log in using a personal laptop. In this scenario, after entering the password, the system prompts for an additional factor (e.g., an OTP via a mobile app or SMS).
- High-Risk Access: The employee is in a foreign location and tries to access the account from an unknown device. In such a situation, access may be blocked, or the employee may have to complete multiple verification steps (e.g., answering security questions, adding an OTP, obtaining admin approval, or using biometric verification).
Setting Up MFA in Auth0
To enable MFA in Auth0:
- Create a tenant and corresponding application.
- Log in to the Auth0 dashboard.
- Navigate to the Security section.
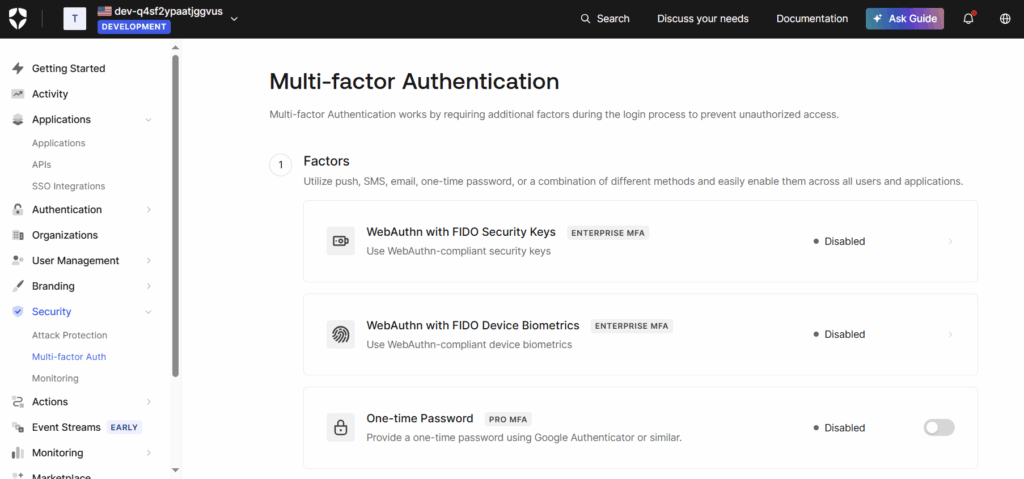
- “Enable MFA and configure desired factors”. Auth0 supports multiple MFA methods. Some commonly used methods are as follows:
- SMS: Sends a verification code to the user’s phone.
- Email: Sends a code to the user’s email.
- Push Notifications: Uses the Guardian app.
- OTP: Generates time-based codes for verification.
Auth0 Built-In Database & User Migration
Auth0’s built-in database is a core feature used for managing user credentials, profiles, and authentication flows. By using this database, you can benefit from tight integration with Auth0’s features (like password reset, multifactor authentication, and account linking). Some of the key capabilities and migration options are as follows:
- Dashboard or Management API: Allows you to create, read, update, and delete users.
- Bulk Migration: Enables you to import users from an existing database. This is a one-time import of all user records into the Auth0 built-in database.
- Lazy Migration: Lets you authenticate users via a custom script and migrate them upon successful login. Users are migrated on first login. If authentication is successful, Auth0 automatically creates the user in the built-in database and stores their credentials.
Auth0 MFA APIs
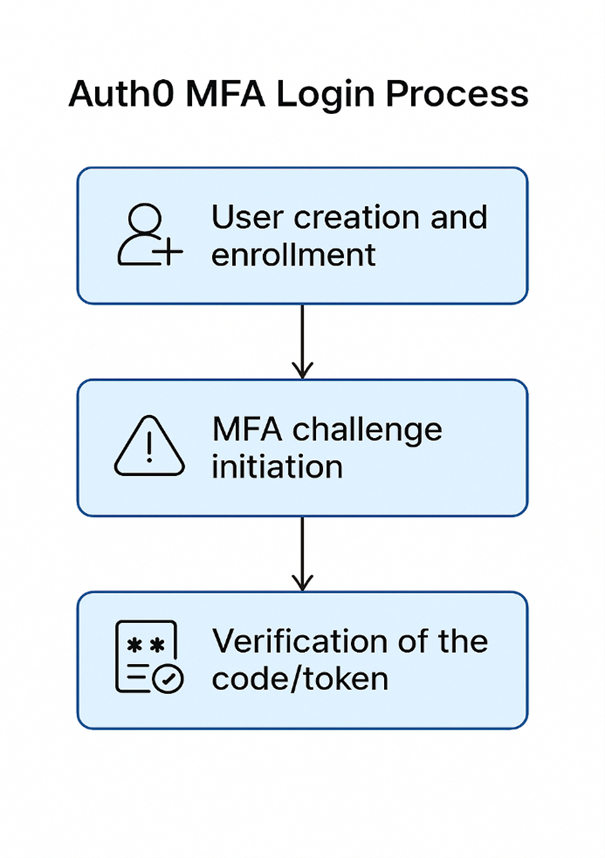
Auth0 provides a set of APIs to help developers integrate Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) into their applications. These APIs give you control over user enrollment, initiating challenges, and verifying MFA tokens. There are three main MFA APIs offered by Auth0:
A. Enrollment API:
Enrollment API lets you enroll users into MFA using authenticator apps (TOTP), email, SMS, and other factors. The key endpoints of this API are:
- POST /api/v2/guardian/enrollments/ticket: Creates an enrollment ticket for the user (for example, to enroll in TOTP).
- GET /api/v2/guardian/enrollments: Lists all MFA enrollments for a user.
- DELETE /api/v2/guardian/enrollments/{id}: Unenrolls a user from a factor.
- POST /mfa/associate: User-driven and enrolls the user in a factor (TOTP, SMS, push notifications, and email).
B. Challenge API:
Challenge API enables you to initiate an MFA challenge (e.g., send a push notification or SMS code). The key endpoint of this API is POST /mfa/challenge, which initiates an MFA challenge for a user.
C. Verification API:
Verification API allows you to verify the response (MFA token or code) from the user. The key endpoints of this API are:
- POST /oauth/token: Uses this with the MFA token grant type (http://auth0.com/oauth/grant-type/mfa-otp) to complete login after MFA.
- POST /mfa/verify: Verifies an MFA challenge response.
Passwordless Authentication with Auth0
Passwordless authentication allows users to log in using a one-time code or magic link sent via email or SMS, eliminating the need to remember or manage passwords. This approach helps:
- Reduce risk of password theft, reuse, and phishing
- Minimize risks of attack vectors since no passwords are stored
- Remove the complexity of remembering complex passwords
- Enables faster and simpler login process
Auth0 Passwordless APIs
The key passwordless authentication APIs provided by Auth0 are:
- POST /passwordless/start: It initiates the passwordless login flow by sending a magic link or one-time code to the user via email or SMS.
- POST /oauth/token: It completes the login by verifying the code or magic link and issuing an access token.
Auth0 MFA vs Passwordless
Ideal Scenarios for Auth0 MFA
| Use Case | Why is Auth0 MFA Ideal? |
| Workforce Authentication (Employees and Admins) | Adds strong protection for admin portals, cloud infrastructure, and internal tools. Auth0 supports adaptive MFA and is triggered based on risk. |
| B2B Apps with Role-Based Access Control | Enforces MFA for high-privilege roles (like finance and admin) using Auth0’s conditional access and rules. |
| Remote or International Logins | Uses adaptive MFA to prompt for extra verification if login device, location, or time is unusual. |
Ideal Scenarios for Passwordless
| Use Case | Why is Passwordless Ideal? |
| Consumer Apps (B2C) with Casual Users | Avoids password fatigue and reset requests. A magic link via email or SMS offers fast access. |
| Internal Tools with Small Teams | Reduces IT overhead by using email or SMS login instead of managing passwords and resets. |
| Regions or Users with Low Tech Literacy | Enables non-technical users to easily log in by clicking a magic link or entering an SMS code, rather than managing complex passwords. |
Alternatives to Auth0 MFA
While Auth0 offers a robust solution, there are alternatives available for developers with budget constraints. These include open-source identity providers or custom-built MFA systems. Some alternatives are AWS Cognito, Firebase Authentication, Keycloak, Okta, and more.
| Platform | MFA Support | Open Source | Best For | Notes |
| AWS Cognito | Yes | No | AWS Ecosystem | – Integrates well with AWS services – Scalable – Supports SAML/OIDC |
| Firebase Authentication | Yes | No | Startups | – Easy integration with Google services – Good for mobile/web apps |
| Keycloak | Yes | Yes | Self-hosting | – Customizable – Open-source – Supports SSO, LDAP, and social logins |
| Okta | Yes | No | Enterprises | – Compliance features – Enterprise-grade IAM – Extensive integrations |
Conclusion
Auth0 provides a comprehensive and developer-friendly approach to implementing MFA and passwordless authentication. Whether you’re building a small app or a large enterprise solution, Auth0’s tools and APIs make it easier to secure user identities and protect sensitive data. By using Auth0, developers can focus more on building application features while relying on a proven system for managing user identities and access.




